As gaming technology evolves, the demand for optimized system performance continues to grow. One critical factor influencing gaming performance is memory management, particularly the optimization of the memory standby list.
The memory standby list is a feature in Windows operating systems that caches data for quick access. While it can improve system responsiveness, excessive standby memory can lead to issues such as stuttering, lags, and reduced gaming performance.
This guide explores the concept of the memory standby list, its impact on gaming, and strategies for optimizing it to enhance gaming performance.
Table of Contents
What is the memory standby list?
The memory standby list in Windows refers to cached data stored in RAM that the operating system deems potentially useful for future operations. This includes application code, filesystem cache, and other unused physical memory. The standby list allows Windows to quickly access frequently used data without reloading it from storage, thereby improving overall system performance (WindoQ, 2025).
However, the standby list can grow excessively large during prolonged gaming sessions, occupying significant portions of RAM. This can result in reduced usable memory for active processes, causing micro-stutters, performance drops, and even system instability (Tom's Hardware Forum, 2022).
The impact of the memory standby list on gaming
1. Stuttering And performance Drops
When gaming, the system requires a significant amount of free RAM to process textures, assets, and other game-related data. If the standby list occupies too much memory, the system may struggle to allocate resources efficiently, leading to stuttering and frame drops (Steam Community, 2025).
2. Reduced Responsiveness
Excessive standby memory can delay the system's ability to allocate resources to new applications or processes. This is particularly problematic in high-performance gaming scenarios, where real-time responsiveness is crucial (WindoQ, 2025).
3. Memory Leaks and Paging
High standby memory usage can exacerbate memory leaks, forcing the system to rely on paging (using the hard drive or SSD as virtual memory). This significantly slows down performance, as storage access is much slower than RAM (Tom's Hardware Forum, 2022).
Strategies for optimizing the memory standby list
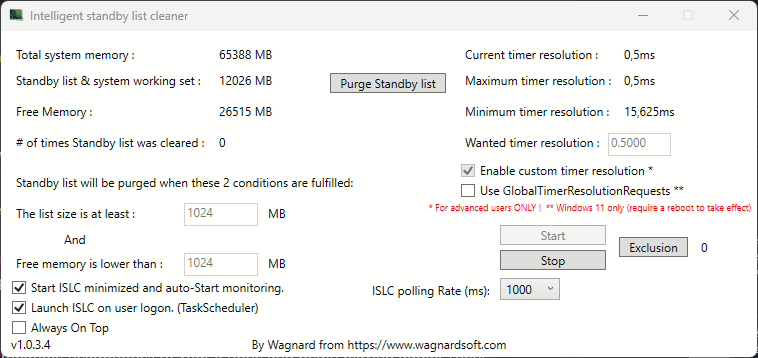
1. Using Intelligent standby list cleaner (ISLC)
The Intelligent Standby List Cleaner (ISLC) is a popular tool designed to monitor and clear the memory standby list based on user-defined thresholds. By default, ISLC purges the standby list when it exceeds 1GB or when free memory drops below 1024MB. These thresholds can be customized to suit specific gaming needs (Wagnardsoft, 2025).
Benefits of islc:
- Automatic Management: ISLC runs in the background, ensuring that the standby list remains within acceptable limits without manual intervention.
- Improved Gaming Performance: By maintaining adequate free memory, ISLC reduces stuttering and enhances frame rates during gaming sessions.
- Low Resource Usage: The tool is lightweight and has minimal impact on CPU and system resources (Wagnardsoft, 2025).
2. Manual Clearing of the standby List
For users who prefer not to use third-party tools, the standby list can be cleared manually using utilities like RAMMap. This method provides greater control but requires regular monitoring and intervention (AddictiveTips, 2025).
Steps to clear the standby list manually:
- Download and run RAMMap (requires administrative privileges).
- Navigate to the "Empty" menu and select "Empty Standby List."
- Monitor memory usage to ensure optimal performance.
3. Adjusting Windows Settings
Windows provides built-in tools and settings to optimize memory management. These include:
- Disabling SysMain (SuperFetch): SysMain preloads frequently used applications into memory, which can inflate the standby list. Disabling this service can free up memory for gaming (WindoQ, 2025).
- Reducing Startup Applications: Limiting the number of background applications reduces memory usage and prevents the standby list from growing excessively (WindoQ, 2025).
4. Upgrading Hardware
While software optimizations can improve performance, upgrading hardware remains the most effective solution for memory-related issues. Increasing the amount of physical RAM ensures that the system has sufficient resources to handle both the standby list and active processes (Tom's Hardware Forum, 2022).
Best practices for memory optimization in gaming
- Monitor Memory Usage Regularly
Use Task Manager or Resource Monitor to track memory usage and identify potential issues with the standby list (WindoQ, 2025). - Customize ISLC Settings
Adjust ISLC thresholds based on your system's specifications and gaming requirements. For example, users with 16GB of RAM may set the purge threshold to 2GB (Wagnardsoft, 2025). - Optimize Windows Services
Disable unnecessary services and startup applications to reduce memory usage and improve system responsiveness (WindoQ, 2025). - Upgrade Hardware When Necessary
If software optimizations fail to resolve performance issues, consider upgrading to at least 32GB of RAM for modern gaming (Tom's Hardware Forum, 2022).
Conclusion
Optimizing the memory standby list is a crucial step in enhancing gaming performance, particularly for users experiencing stuttering, lags, or frame drops. Tools like Intelligent Standby List Cleaner provide automated solutions, while manual methods and Windows settings offer additional flexibility.
However, the effectiveness of these strategies depends on the user's system specifications and gaming requirements. For long-term performance improvements, upgrading hardware remains the most reliable solution.
By implementing these strategies, gamers can achieve smoother gameplay and maximize the potential of their systems.