Analog stick drift, commonly referred to as "stick drift," is a prevalent issue that affects gaming controllers across various platforms, including Xbox, PlayStation, Nintendo Switch, and PC. This phenomenon occurs when the analog sticks register unintended movements without any user input, causing characters or cursors to move erratically on-screen. Stick drift can significantly hinder gameplay, leading to frustration for casual and competitive gamers alike.
The root causes of stick drift are multifaceted, ranging from mechanical wear and tear to environmental factors. Over time, components such as potentiometers and springs within the analog stick assembly degrade due to repeated use. Additionally, the accumulation of dust, debris, or grime around the analog stick mechanism can interfere with its functionality. For a deeper understanding of the technical aspects, the ALPS analog stick potentiometer is a critical component often linked to this issue.
External factors, such as dropping or physically impacting the controller, can also displace internal components, exacerbating the problem. Research from 33rd Square highlights how sudden impacts can knock the analog stick out of calibration, leading to immediate drift issues. Furthermore, outdated firmware or software glitches can contribute to the problem, as noted in discussions on platforms like Reddit.
Despite its widespread occurrence, stick drift is not an insurmountable problem. Various solutions exist, ranging from simple cleaning methods to advanced repairs. Cleaning the analog stick with isopropyl alcohol or compressed air, as detailed in guides like Tim Gadget Log, can often resolve minor drift issues. For more severe cases, recalibrating the controller, updating firmware, or replacing the analog stick module may be necessary.
Preventative measures, such as regular maintenance and proper storage, can also help mitigate the risk of stick drift. Resources like Early Finder emphasize the importance of keeping controllers clean and avoiding excessive force during gameplay to prolong their lifespan.
This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of analog stick drift, exploring its causes, prevention strategies, and step-by-step solutions. By understanding the underlying mechanics and adopting proactive measures, gamers can restore their controllers' precision and enhance their overall gaming experience.
Table of Contents
Causes of analog stick drift
Mechanical wear and tear
One of the primary causes of analog stick drift is the mechanical degradation of components over time. Analog sticks rely on potentiometers to measure the position of the joystick. Potentiometers are essentially variable resistors with a wiper that moves along a resistive track. Over extensive use, the following issues can arise:
- Material Fatigue: The resistive material within the potentiometer can degrade, leading to inaccurate readings. For example, a potentiometer with an ideal resistance of 10k ohms might show deviations, such as 9.5k ohms overall resistance, with imbalances between the wiper and output pins (e.g., 5.5k ohms vs. 5.3k ohms). This imbalance causes the controller to misinterpret the joystick's neutral position (Instructables).
- Spring Mechanism Weakening: Springs inside the analog stick assembly are responsible for returning the joystick to its neutral position. Over time, these springs can lose tension, resulting in the stick failing to return to its center accurately.
The wear and tear of these components are inevitable with regular use, particularly in controllers subjected to high-intensity gaming sessions or frequent directional inputs.
Dust and debris accumulation
Environmental factors, such as dust and debris, play a significant role in causing analog stick drift. Dust particles and other contaminants can infiltrate the analog stick housing and disrupt its functionality. Key points include:
- Impact on Potentiometers: Dust can settle on the resistive track of the potentiometer, creating electrical interference. This contamination can lead to erratic resistance values, causing the controller to register unintended movements (Gaming Pedia).
- External Contaminants: Substances like grease from hands, crumbs from food, or pet hair can exacerbate the problem. These contaminants can obstruct the movement of the joystick or interfere with the electrical signals.
- Prevention Measures: Keeping controllers in clean environments, covering them with microfiber cloths when not in use, and avoiding eating or drinking near them can reduce the likelihood of dust-related drift (Gaming Pedia).
Potentiometer design limitations
The design of potentiometers in analog sticks inherently contributes to drift over time. While this topic overlaps with mechanical wear, it specifically highlights the limitations of the technology used:
- Resistance Imbalances: Even in brand-new controllers, potentiometers may not achieve perfect resistance values. For example, a new potentiometer might deviate slightly from the ideal 5k ohms resistance between the wiper and each output pin. These imperfections can worsen with use, leading to drift (Instructables).
- Manufacturing Variances: Small inconsistencies during production can result in potentiometers that are more prone to drift. These variances may not be noticeable initially but can become problematic as the controller ages.
Software and firmware issues
While analog stick drift is predominantly a hardware issue, software and firmware can occasionally contribute to the problem:
- Calibration Errors: Improper calibration of the analog stick can cause the controller to misinterpret the joystick's position. This is particularly common after firmware updates or when switching between devices (Codefiner).
- Deadzone Settings: Deadzones are areas within the joystick's range of motion where input is ignored. If the deadzone is too small, minor deviations caused by hardware imperfections can result in drift. Adjusting the deadzone settings in games or controller software can mitigate this issue temporarily.
Environmental and user-handling factors
External factors, including the environment and how users handle their controllers, can also influence the occurrence of analog stick drift:
- Humidity and Temperature: Changes in humidity and temperature can affect the materials within the analog stick assembly. For instance, high humidity may cause dust to clump together, increasing the likelihood of interference with the potentiometer (Codefiner).
- Handling Habits: Rough handling, such as forcefully pressing or moving the joystick, can accelerate wear and tear. Additionally, storing controllers in dusty or damp environments can increase the risk of drift.
Electrical signal disruptions
Analog stick drift can also result from disruptions in the electrical signals sent by the joystick to the controller's circuit board. These disruptions may stem from:
- Worn Connections: The electrical connections between the potentiometer and the circuit board can degrade over time, leading to inconsistent signal transmission.
- Voltage Variations: Variations in the voltage supplied to the potentiometer can cause the controller to misinterpret the joystick's position. This issue is more common in older controllers or those with damaged internal wiring (Instructables).
Component design trade-offs
The design of modern gaming controllers often involves trade-offs between cost, durability, and performance. These trade-offs can indirectly contribute to stick drift:
- Cost Constraints: To keep controllers affordable, manufacturers may use components that are not optimized for long-term durability. For instance, potentiometers with lower-grade materials are more susceptible to wear and tear.
- Compact Designs: The compact design of modern controllers leaves little room for robust protective measures against dust and debris. This makes the internal components more vulnerable to environmental factors.
By understanding these causes, both manufacturers and consumers can take steps to mitigate analog stick drift. Manufacturers can focus on improving component durability and design, while consumers can adopt preventive measures to prolong the lifespan of their controllers.
Methods to fix analog stick drift
Cleaning the analog stick assembly
Dust and debris are common culprits behind analog stick drift. Cleaning the analog stick assembly can often resolve the issue without requiring advanced tools or technical expertise. While the existing content on "Dust and Debris Accumulation" discusses the causes of drift, this section focuses on cleaning as a solution.
- Compressed Air Cleaning:
Use a can of compressed air to blow around the analog stick base. Rotate the stick while spraying to dislodge debris trapped inside. This method is effective for removing fine particles that interfere with the potentiometer. (Games Learning Society) - Isopropyl Alcohol Cleaning:
Dip a cotton swab in isopropyl alcohol (preferably 90% or higher) and gently clean around the base of the analog stick. This removes grease, grime, or stubborn debris that compressed air might miss. Allow the alcohol to evaporate completely before testing the controller. (Hablamos de Gamers) - Preventative Maintenance:
Regular cleaning every few months can prevent debris build-up. Avoid eating or drinking near controllers and store them in clean, dust-free environments. These measures reduce the risk of future drift. (Gaming Pedia)
Recalibrating the controller
Recalibration addresses software-related inaccuracies in joystick input detection. While the existing content on "Software and Firmware Issues" explains calibration errors as a cause, this section focuses on recalibration as a corrective measure.
- Manual Recalibration:
Most gaming platforms offer built-in tools to recalibrate controllers. For example:
- On Xbox Series X, navigate to Settings > Devices & Accessories > Controllers and follow the on-screen instructions to recalibrate. (Games Learning Society)
- On PS5, connect the controller via USB, go to Settings > Devices > Controllers, and select "Reset Controller Calibration." (Hablamos de Gamers)
- Game-Specific Deadzone Adjustments:
Some games allow players to adjust the deadzone settings, which define the range of joystick motion ignored by the system. Increasing the deadzone can mask minor drift issues by requiring greater stick movement before registering input. (wikiHow) - Firmware Updates:
Ensure the controller's firmware is up-to-date. Firmware updates often include bug fixes and performance improvements that can resolve calibration issues. (Games Learning Society)
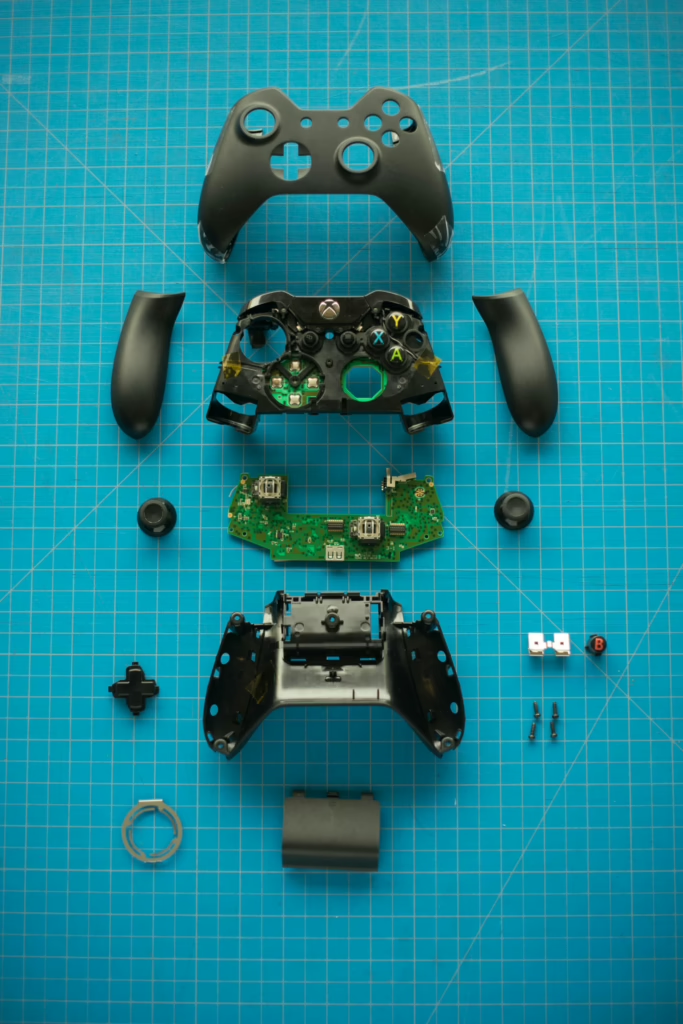
Repairing or replacing internal components
When cleaning and recalibration fail, the issue may lie with worn or damaged internal components. This section expands on the topic of "Mechanical Wear and Tear" by detailing repair and replacement methods.
- Replacing the Potentiometer:
The potentiometer, a key component in detecting joystick movement, is prone to wear over time. Replacing it requires soldering skills and access to replacement parts, which can be purchased online. This repair is cost-effective compared to buying a new controller but voids the warranty. (LifeWire) - Analog Stick Replacement Kits:
Pre-packaged repair kits for analog sticks are available for popular controllers like the Xbox Series X, PS5, and Nintendo Switch. These kits include the necessary tools and components, making the repair process more accessible to non-experts. (ExpertBeacon) - Professional Repair Services:
If DIY repairs are not feasible, professional repair services can replace damaged components. Many manufacturers, including Microsoft and Sony, offer repair programs for controllers under warranty. For out-of-warranty repairs, third-party services are an alternative. (Games Learning Society)
Adjusting user habits and handling
While the existing content on "Environmental and User-Handling Factors" highlights causes, this section focuses on behavioral adjustments to prevent and mitigate stick drift.
- Avoid Excessive Force:
Applying excessive pressure to the analog stick can accelerate wear and tear. Use gentle, deliberate movements during gameplay to prolong the lifespan of the joystick. (Games Learning Society) - Rotate Sticks Regularly:
Periodically rotate the analog sticks in full circles to distribute wear evenly across the potentiometer. This simple habit can delay the onset of drift. (wikiHow) - Proper Storage:
Store controllers in a clean, dry environment away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Use protective cases or covers to shield them from dust and debris. (Gaming Pedia)
Exploring alternative technologies
This section introduces alternative technologies that could reduce the prevalence of analog stick drift, complementing the discussion on "Component Design Trade-offs."
- Hall Effect Sensors:
Unlike potentiometers, Hall effect sensors use magnetic fields to detect joystick movement. These sensors are more durable and less prone to wear but are currently more expensive to implement. Some third-party controllers already use this technology. (Nerd Techy) - Capacitive Touch Joysticks:
Capacitive touch technology, commonly used in touchscreens, could replace traditional analog sticks. This approach eliminates moving parts, reducing the risk of mechanical failure. However, it may lack the tactile feedback gamers expect. (ExpertBeacon) - Modular Controller Designs:
Modular controllers with easily replaceable analog sticks are gaining popularity. These designs allow users to swap out faulty components without disassembling the entire controller, simplifying repairs. (Games Learning Society)
By implementing these methods and exploring emerging technologies, gamers can address and potentially prevent analog stick drift in their controllers.
Preventive measures for analog stick drift
Regular maintenance practices
To minimize the risk of analog stick drift, routine maintenance is essential. While some aspects of maintenance overlap with previously discussed cleaning methods, this section focuses on additional preventive measures that go beyond basic cleaning.
Lubricating analog stick mechanisms
Applying a small amount of non-conductive, electronics-safe lubricant to the analog stick's moving parts can reduce friction and wear over time. This practice is especially effective in controllers that experience heavy use. Ensure the lubricant is applied sparingly to avoid attracting dust or debris. This method is distinct from cleaning techniques like using isopropyl alcohol, as it focuses on reducing mechanical wear rather than removing contaminants. (HBZ Guide)
Periodic internal inspections
Opening the controller periodically (if the warranty allows) to inspect the internal components for signs of wear, dust, or debris can help catch potential issues early. Use an anti-static brush to clean sensitive areas during inspections. This preventive measure is more proactive compared to external cleaning methods and requires a higher level of technical skill. (Fix It Insider)
Replacing worn components
For controllers with replaceable analog stick modules, replacing the potentiometers or thumbstick assemblies before they fail can prevent drift. This approach requires identifying signs of wear, such as reduced responsiveness or uneven resistance during gameplay. Unlike reactive fixes, this method is preemptive, ensuring consistent performance over time. (ExpertBeacon)
Environmental control
Environmental factors play a significant role in the longevity of gaming controllers. While existing content has touched on the impact of humidity and temperature, this section expands on creating an optimal storage and usage environment.
Controlled storage conditions
Store controllers in an environment with stable temperature and humidity levels. Use silica gel packets in storage containers to absorb excess moisture, which can lead to dust clumping and potentiometer interference. This is a more advanced storage solution compared to simply keeping controllers in a dry place. (Games Learning Society)
Minimizing exposure to particulates
Avoid using controllers in environments with high levels of airborne particulates, such as near open windows or in rooms with ongoing construction. Using protective covers or cases when the controller is not in use can further shield it from dust and debris. This builds on the idea of proper storage by focusing on active usage environments. (TechFanzine)
Anti-static measures
Static electricity can damage sensitive electronic components within the controller. Gamers can reduce static buildup by using anti-static mats or wrist straps when handling controllers, particularly during cleaning or maintenance. This preventive measure is unique and not covered in existing content. (Fix It Insider)
Optimizing controller settings
Adjusting software settings can help mitigate the effects of drift and prolong the usability of the controller. This section focuses on preventive adjustments rather than reactive fixes like recalibration.
Increasing deadzone settings
Increasing the deadzone in games or controller software can prevent minor deviations from being registered as input. While this does not eliminate drift, it reduces its impact on gameplay. This approach complements hardware maintenance by addressing software-level sensitivity. (GamersWiki)
Customizing sensitivity profiles
Some controllers allow users to create custom sensitivity profiles for different games. Lowering sensitivity in non-critical areas of the joystick's range can reduce wear on potentiometers, thereby delaying the onset of drift. This method is distinct from recalibration, as it focuses on proactive customization. (Games Learning Society)
Firmware updates
Regularly updating the controller's firmware ensures it has the latest bug fixes and optimizations. Manufacturers often release updates to address known issues, including those that may contribute to drift. This preventive measure is more general than recalibration and applies to all users, regardless of whether drift has occurred. (OneSaharan)
Improved handling techniques
Proper handling of controllers can significantly reduce the likelihood of drift. While existing content has discussed avoiding excessive force, this section introduces additional techniques to enhance durability.
Avoiding rapid stick movements
Repeated rapid movements, such as flicking the analog stick during intense gameplay, can accelerate wear on the potentiometer. Gamers should aim for smooth, deliberate movements to reduce strain on internal components. This advice is more specific than general recommendations to avoid rough handling. (HBZ Guide)
Using thumbstick grips
Silicone thumbstick grips can reduce direct wear on the analog stick surface and improve user control. These grips are inexpensive and easy to replace, making them a practical addition to any controller. This method complements existing suggestions for protective covers by focusing on the thumbstick itself. (Fix It Insider)
Rotating controllers
For gamers who own multiple controllers, rotating their usage can distribute wear evenly across devices. This approach is particularly useful for competitive players who put significant strain on their equipment. While similar to rotating analog sticks, this method applies to the entire controller. (ExpertBeacon)
Investing in durable alternatives
For gamers seeking long-term solutions, investing in controllers with advanced technologies can reduce the risk of drift. This section explores alternatives that go beyond traditional analog stick designs.
Hall effect joysticks
Controllers equipped with Hall effect sensors use magnetic fields to detect movement, eliminating physical contact between components. This design significantly reduces wear and is increasingly available in premium controllers. While previously mentioned as an alternative technology, this section emphasizes its preventive benefits. (Nerd Techy)
Modular controllers
Some manufacturers offer controllers with modular analog sticks, allowing users to replace worn components without disassembling the device. This feature extends the controller's lifespan and reduces maintenance costs. This approach is distinct from replacing components in traditional controllers, as it requires no technical expertise. (TechFanzine)
Premium build materials
High-end controllers often use more durable materials, such as metal housings and reinforced potentiometers, to withstand heavy use. While these controllers are more expensive, their longevity can offset the initial investment. This method focuses on preventive durability rather than reactive fixes. (ExpertBeacon)

Conclusion
Analog stick drift, a prevalent issue in gaming controllers, arises from a combination of mechanical wear, environmental factors, design limitations, and occasional software inaccuracies. The primary causes include the degradation of potentiometers due to material fatigue, weakening of internal springs, and the accumulation of dust and debris, which disrupt electrical signals and joystick functionality. Design trade-offs, such as cost constraints and compact layouts, further exacerbate the problem, while improper calibration and inadequate deadzone settings can amplify the effects of drift. External factors, such as rough handling, humidity, and temperature fluctuations, also contribute to the issue, highlighting the multifaceted nature of this challenge.
Addressing analog stick drift requires a combination of corrective and preventive measures. Cleaning the analog stick assembly with compressed air or isopropyl alcohol can resolve minor issues, while recalibration and firmware updates address software-related inaccuracies. For more severe cases, replacing worn components like potentiometers or utilizing professional repair services may be necessary. Preventive strategies, such as regular maintenance, proper storage, and adopting improved handling habits, can significantly reduce the likelihood of drift. Moreover, exploring alternative technologies like Hall effect sensors, modular controller designs, and capacitive touch joysticks offers promising long-term solutions to mitigate this issue. These advancements, while potentially more expensive, provide enhanced durability and performance compared to traditional potentiometer-based designs.
The implications of this research suggest that both manufacturers and consumers have roles to play in combating analog stick drift. Manufacturers should prioritize the development of more durable components and explore innovative technologies to minimize drift, while consumers can adopt better maintenance practices and handling techniques to prolong the lifespan of their controllers. As gaming technology evolves, integrating advanced sensor technologies and modular designs into mainstream controllers could redefine industry standards, offering gamers more reliable and sustainable hardware. For more details on preventive measures and emerging solutions, refer to resources like Games Learning Society and Nerd Techy.

